Introduction
The European Capacity Management Tool (ECMT) is an online application providing a centralised capacity supply and capacity model overview of railway lines and routes. The tool consolidates capacity needs and capacity restrictions on the railway infrastructure based on the information provided by Infrastructure Managers and Allocation Bodies. It offers the capacity supply and the capacity model visualisations and other related functionalities.
ECMT was first launched as part of the Timetable Redesign (TTR) Pilots, and in the future, it will also intend to play the role of the capacity hub in the TTR IT Landscape.
The aim of the following documentation is to give an overview of ECMT structure, functionalities and constraints.
1. Access to ECMT
1.1 ECMT account, login and password reset.
New account request, login and password reset are available on the ECMT home page.

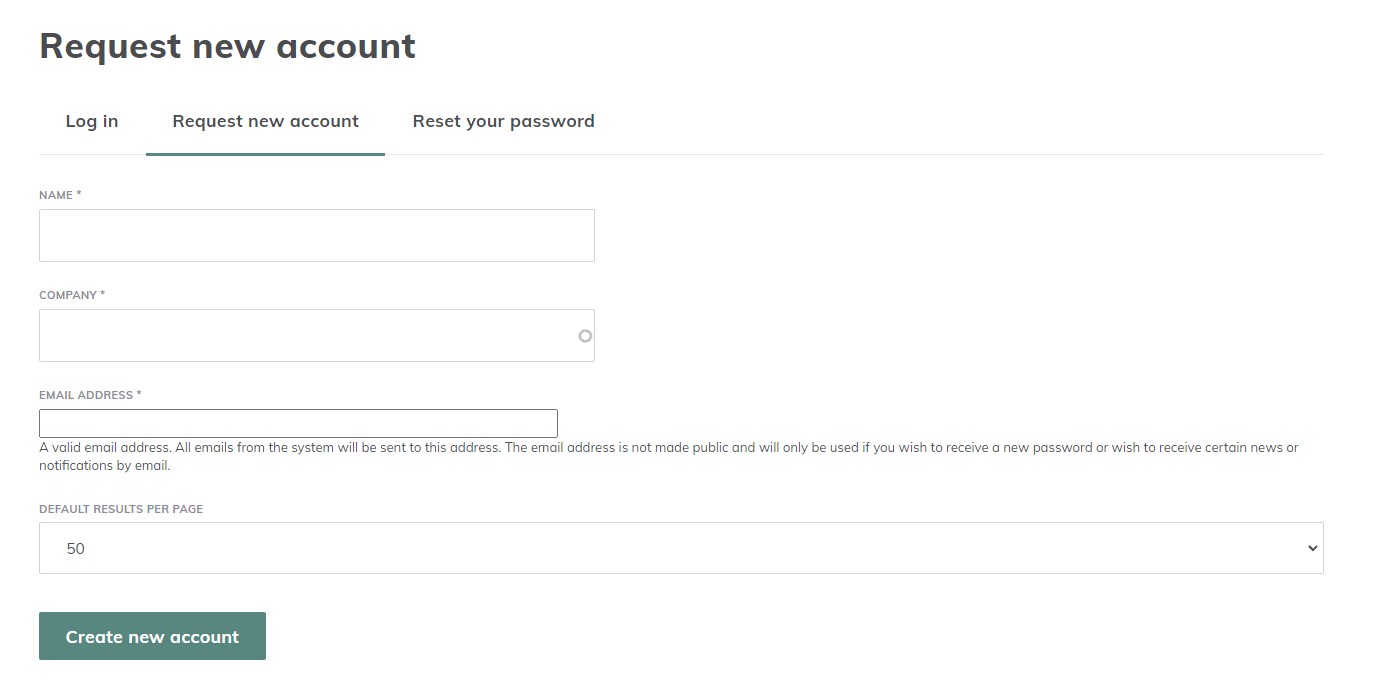
1.1.1 Request a new ECMT account
The request for the creation of an ECMT account can be sent via the online form available on the ECMT homepage after clicking on “Request new account” or by sending an email to the ECMT support team: support.ecmt@rne.eu.
The requests are reviewed by the ECMT support team. Once the request is approved, the requester will receive the login credentials per email.
1.1.2 Password reset
The user provides his/her email address. The email with the instructions for the password reset will be shortly received.
1.1.3 Login
The email address provided in the new account request and the password after the account creation, need to be entered on the ECMT home page.
1.2 Access rights
Based on the user’s company (selected in the registration step), and the company’s attributes defined in CRD (The Central Reference File Database), the user will be defined as either “IM” or as “Applicant”.
If the user belongs to an Infrastructure Manager company, they would be able to define Capacity Model data objects for PLCs which belong to their network (and no other IM, unless defined in Access Right Module).
In case the user belongs to an Applicant company, the user is be able to define the Capacity Needs Announcement.
The following menus, functions, and information are publicly available with an anonymous profile and do not require an ECMT account:
- Capacity Supply Chart
- Capacity Model
- Segment Overview
- Line Overview
- Network Overview
- Only objects with a “published” status are visible on: charts, in search results and their object page.
The following user roles are available and provide the following additional features:
- Read-only role: custom save search
- Editor role: all objects are visible and objects in the preparation phase are editable.
With an editor role, the editing rights on an object are available if the user is an editor on all the lines that are used by the route of the object. If the user is not an editor on at least one part of the route, the object will be read-only.
1.3 Access rights module
In this menu, IM users with the aforementioned mentioned Editor role can give members of other companies permission to view and/or edit objects of their company. These rights can either be given permanently or for a limited amount of time and can be revoked at any point. Additionally, users can give these permissions to all users of a company at once, in case two companies share a physical network and its responsibilities. Access rights for other companies cannot be requested in the tool, they can only be given to others.
Users from a company which has given its rights to a 3rd party can see what user/companies have access to their data.
2. ECMT Menus
ECMT navigation is organised around two menus for anonymous users, four menus for users with a read-only role and five menus for users with an editor role.
![]()
2.1 +Add CNA
This menu is a shortcut for Applicant users to quickly create CNAs (Capacity Needs Announcements). CNAs can also be created, imported, viewed, and edited (depending on user rights) from the 'data' menu (see section 2.5).
2.2 Overview
This menu lists all objects, which have been created or edited by the user. A detailed view of these objects can be accessed using the links provided in the same rows as them. The Overview page can also be found under “My profile”.
2.3 ECMT Tabfolder
This menu contains all the items from Capacity Model and Capacity Supply, as well as the TCR Duration Overview:

2.3.1 Capacity Model
The Capacity Model contains three overviews:
- Segment Overview: Capacity situation between two PLCs (e.g. to gather information on the planned volumes for a border section). Mostly used by Applicants.
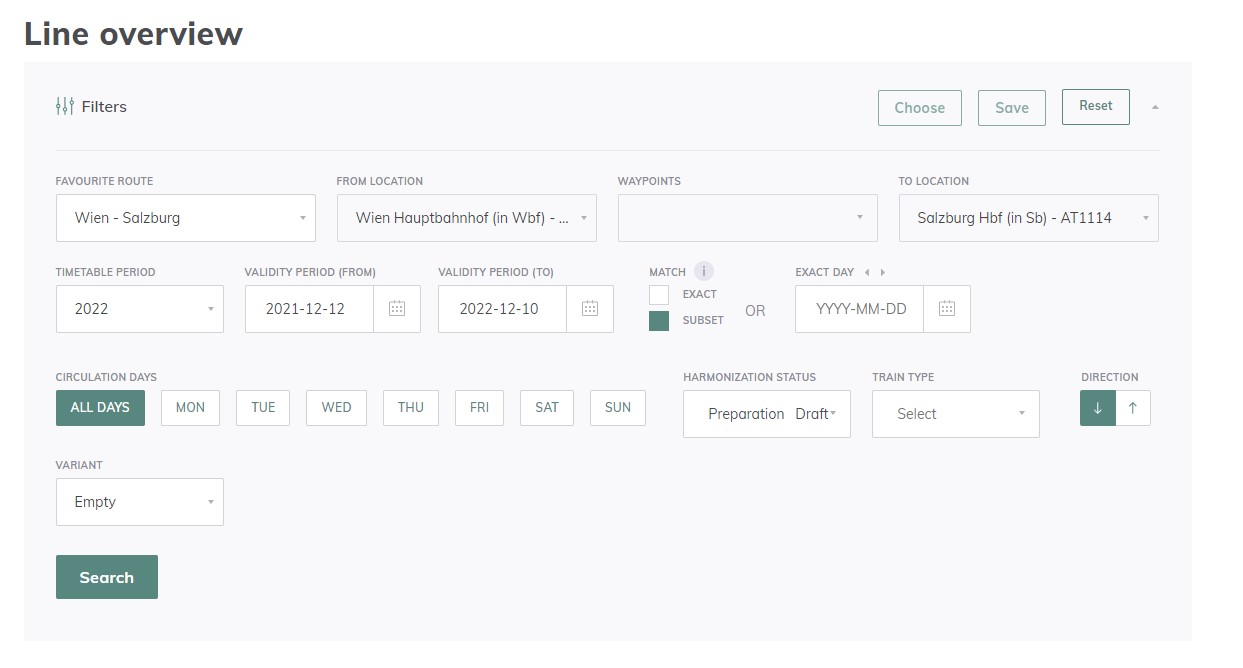
- Line Overview: Capacity situation on a selected line to facilitate cross-border harmonisation and creation of variants (e.g. during TCR periods). Mostly used by IMs, Applicants
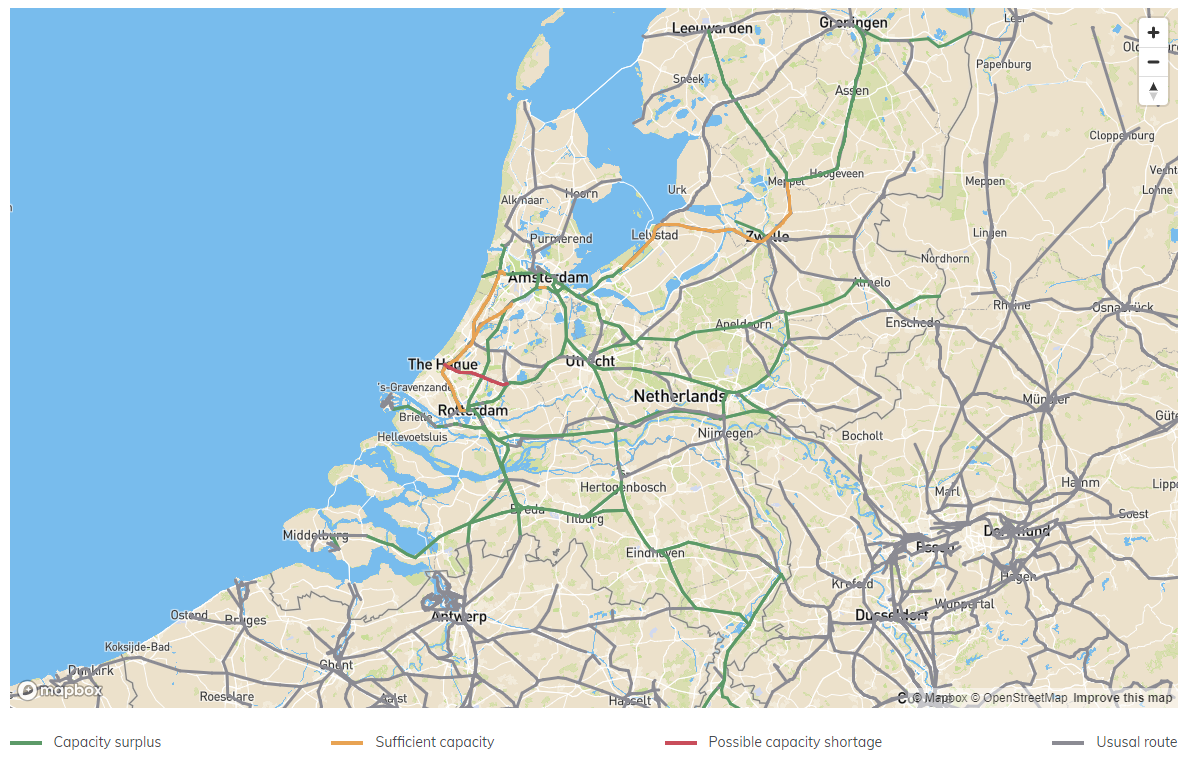
- Network Overview: General overview of capacity on a very high level (e.g. capacity situation of a selected country). Mostly used by higher management levels, Ministry of Transport, etc.
2.3.1.1 Segment Overview
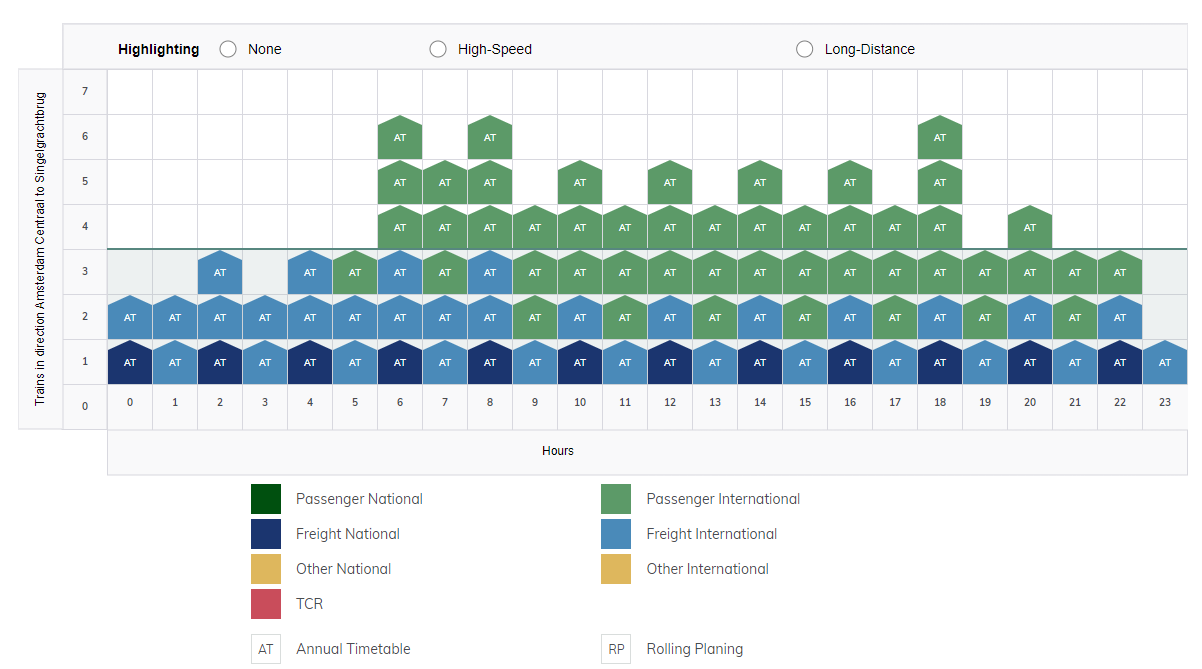
2.3.1.2 Line Overview
2.3.1.3 Network Overview
2.3.2 Capacity Supply Chart
The Capacity Supply Chart visualises Catalogue Paths, Paths, Bandwidths, and TCRs on a time-space diagram. The Capacity Supply allows minute-based visualisation of Capacity Products and provides a detailed overview of the available capacity for different ordering periods on a European scale, as well as a clear view of TCRs and their impact on traffic. The Capacity Supply can be defined for any route.
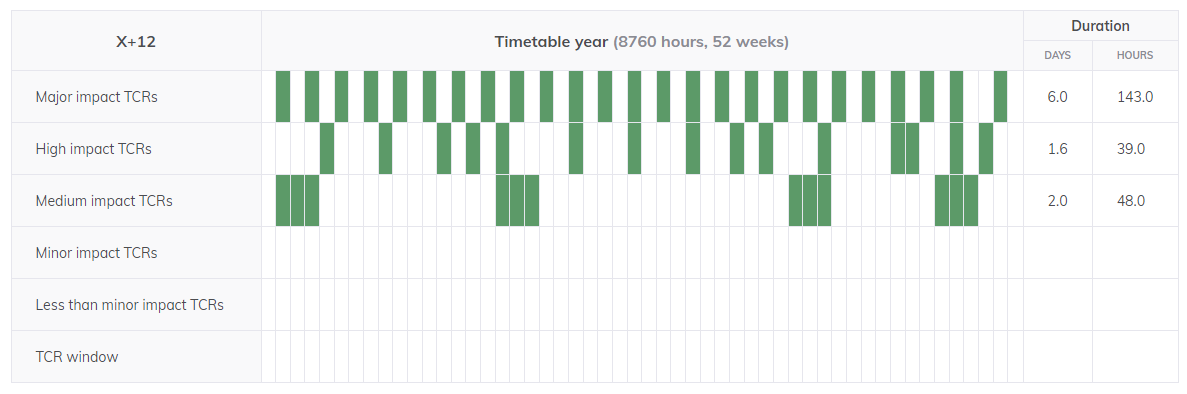
2.3.3 TCR Duration Overview
The TCR Duration Overview provides a 52 week overview of the situation between any two PLCs regarding TCRs.
2.4 Search
This menu contains the search function and the overlapping objects detection feature. Please refer to section 5 for more information.
2.5 Data (available with editor role)
This menu contains the object creation, editing and import functions. Please refer to section 6 for more information.
2.6 My profile (available with read-only and editor roles)
This menu contains the basic information about the user’s account (name, e-mail address etc) and the lines assigned to the user (available for editor roles).
3. Objects
3.1. Object types
- Path: capacity planned for one train.
- Bandwidth: capacity planned for more than one path within a specific timeframe and with a predefined number of capacity slots.
- Catalogue Path: pre-constructed capacity paths prepared by the infrastructure managers and offered to applicants.
- Temporary Capacity Restrictions (TCRs): capacity restriction planned as necessary to maintain the infrastructure and allow development in accordance with market needs.
Users with an editor role can manage the objects they have access to. Please refer to sections 1.2 and 6.1 for more information.
3.2. Object Allocation
Objects can be created between any two PLCs. The user with an editor role selects the allocation type when creating the object, however, all objects (regardless of their allocation) are visible on the line and route time-space charts as well as in the search and overlapping objects detection results list if no specific filter is applied.
3.2. Object allocation
Objects can be created between any two PLCs. The user with an editor role selects the allocation type when creating the object, however, all objects (regardless of their allocation) are visible on the time-space charts as well as in the search and overlapping objects detection results list if no specific filter is applied.
4. Capacity Supply chart
4.1. Structure of the chart
The time-space chart presents the objects positioned between two PLCs according to the chart filters. Time is on the x-axis and the PLCs are listed on the y-axis with spacing considering the actual distance between the locations.
Chart features:
- Route filter: The “From location” and “To location” shall be informed by the user and the tool calculates shortest route between these two locations considering the waypoint (optional field). The tool will generate the chart including objects that are either fully or partially positioned on the generated route. As soon as there is one common location between two lines, the tool assumes the transfer of the train from one to another is possible.
- Zoom sliders: a zoom on a specific line, route or timeline section is possible with the zoom slider bars (thick grey lines above and on the right side of the chart)
- Link to the object page: a click with the mouse on the object positioned on the chart opens the object page in a new tab.
- Tooltip: a mouse hover on the object positioned on the chart shows a tooltip containing basic information about the object.
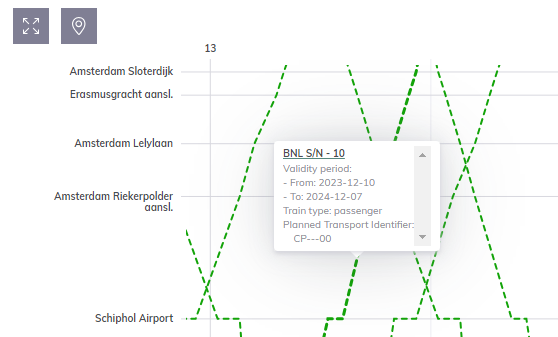
Object representations:
- Passenger Catalogue Path: green dotted line
- Freight Catalogue Path: blue dotted line
- Freight Cataloue Rolling Planning: turquoise dotted line
- Passenger Path: green solid line
- Freight Path: blue solid line
- Capacity Band and TCRs: shape depending on the timetable
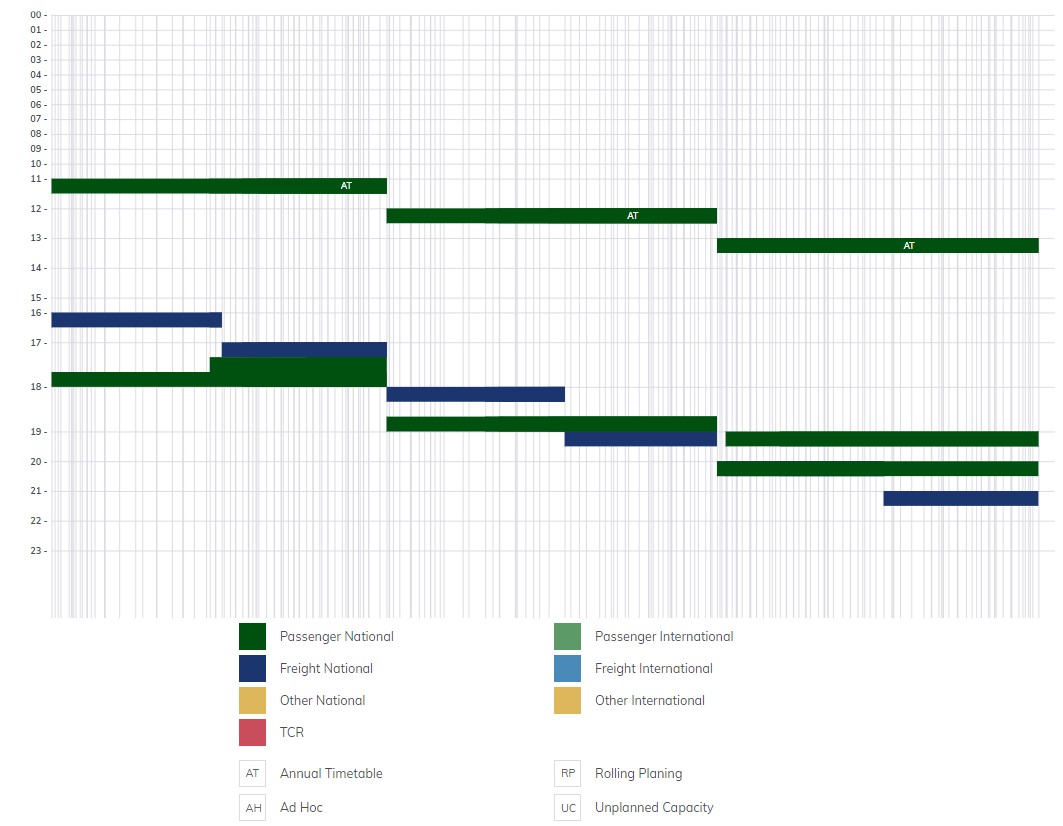
4.2. How to read the chart?
Objects are positioned on the chart based on their timetable.
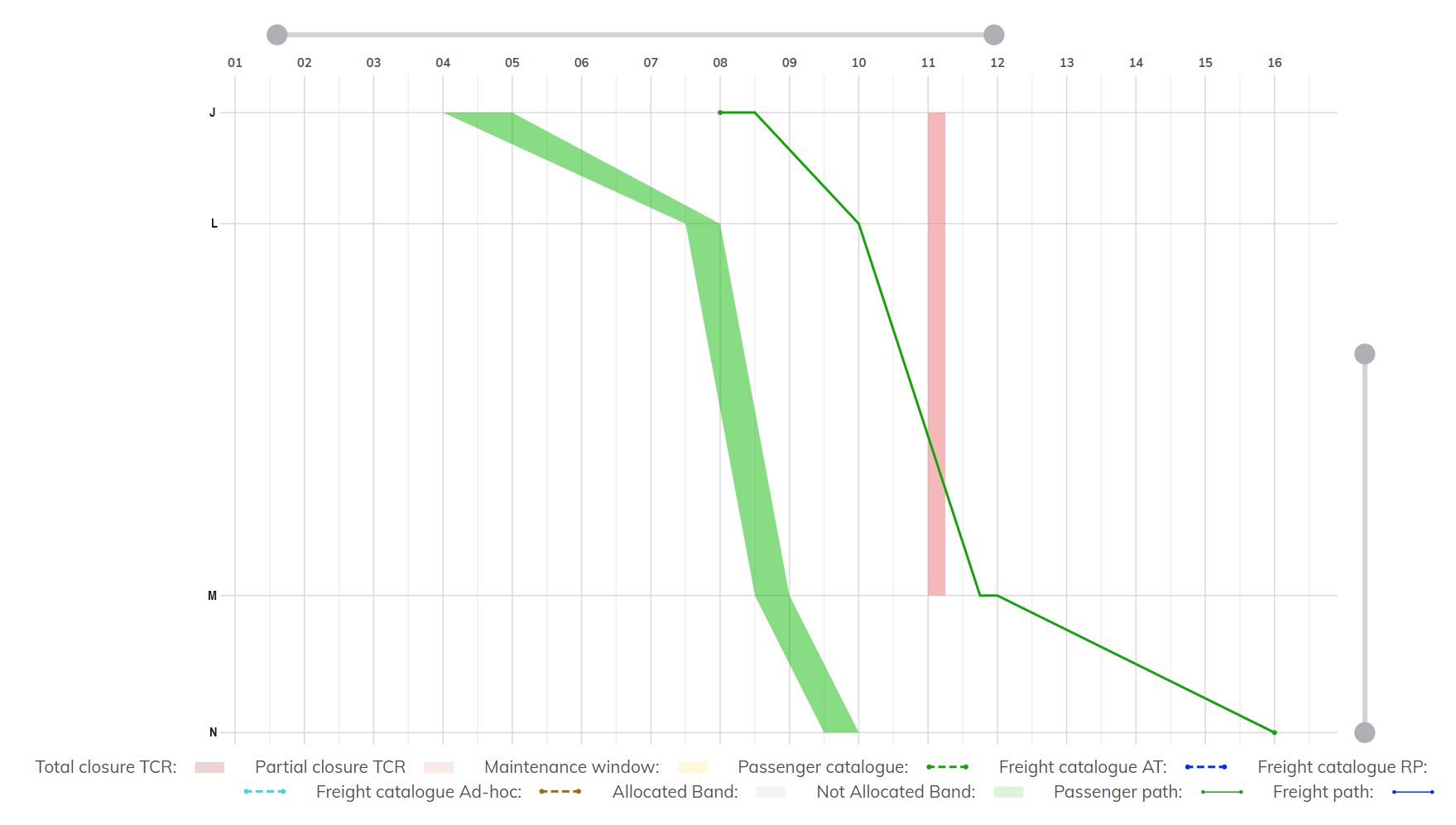
Below is a practical example:
Case:
- First, a path, a TCR, and a bandwidth have been created on a route starting from J, passing by locations L and M and ending at N.
- Secondly, a chart has been generated for a route from A to N via J. The location sequence calculated by the tool for this route is A-B-I-J-L-M-N.
- It is relevant to note that the three created objects are located on the route from A to N via J.
Interpretations:
- The zoom sliders have been adjusted to focus on the J-L-M-N route section between 01:00 and 16:00.
- The legend at the bottom of the chart refers to all objects included on the chart for route A-B-I-J-L-M-N.
- Path - Solid green line: the train arrives at location J at 8:00 and departs at 8:30. Between 11:45 and 12:00 it stays at location M and arrives at location N at 16:00.
- Partial closure TCR - Red bar: TCR between 11:00 and 11:50 between locations J and M.
- Capacity Band – green band: capacity planned with a 30 minute timeframe from location J to N.
4.3. Object positioning over different lines
Objects are defined with a timetable on the entire length or on a partial section of a line, but the object information is stored per location. Therefore, objects may appear either fully, or partially on the other charts and in the search results depending on the selected line and their potential timetable overlap.
5. The search function
5.1. Search function
Search filters are available to refine the search. Search results list all objects according to the search filters. Each object is accessible by clicking on its title, a new tab will open with the object details.
When the “From location” and “To location” are selected by the user, the tool calculates the shortest route between those two locations considering the waypoint(s) (optional field). The tool generates the results list with the objects that are both fully and partially positioned on the route. As soon as there is one common location between an object and the route, the object is listed.
5.2. Export function (available with read-only and editor roles)
Search results can be exported into Excel. This can be done by selecting 'Export to Excel', located at the bottom of the results page.
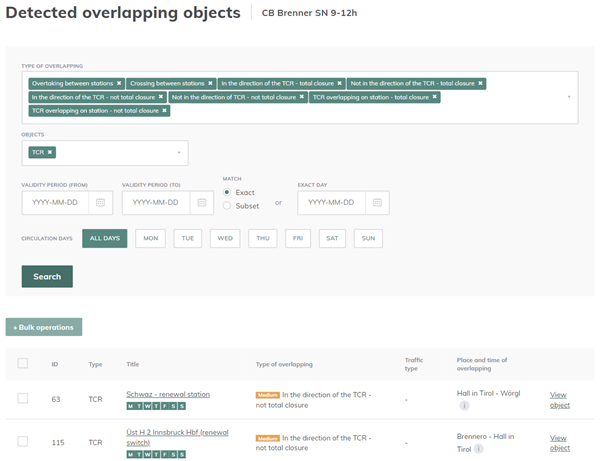
5.3. Overlapping objects detection
The overlapping objects detection feature is accessible at the bottom of object page for Capacity Supply Objects (Paths, Bands, and Catalogue Paths) and TCRs. This feature lists in a new tab the objects which overlap with the selected object. Objects are listed in the results as soon as they have one common location with the selected object.
This feature serves as a means of conflict resolution, however, as the tool has limited information about the infrastructure, it has been named “overlapping detection”. To provide some indication about potential conflict risk, each overlapping object is listed with a priority level. For example, an overlap with a total closure TCR has a high priority, while two paths overlapping each other at a station has low priority because crossing a total closure TCR is very likely to be a critical conflict while overtaking between two stations can happen as planned.
6. Object creation, editing and import (available with editor role)
In the Data menu’s drop-down list, the user has the ability to view, import, create, and edit several types of objects, including:
- Capacity Poducts (CP)
- Temporary Capacity Restrictions (TCRs)
- Bandwidths (Band)
- Paths
- Capacity Model Objects (CMOs)
- Intended Capacity Lines (ICLs)
- Capacity Model Variants
- Capacity Needs Announcements (CNAs)
Once selecting the type of obect which the user would like to manage, a page with the option to import (section 7.2), add/edit an object, object bulk operation (section 7.1.5) and search functions will open.
6.1 Object creation and editing
6.1.1. Search function and general guidelines
Upon selecting any of the above mentioned object types from the 'Data' menu, the page will display a full list of those objects. This list can be filtered and searched from.
6.1.1.1 Search function
The search function contains the same filters and has the same layout as the search function in the search menu. The user can search for objects and edit or choose one of the other operations available in the drop-down list of the column "Operations".
When the “From location” and “To location” are selected by the user, the tool calculates the shortest route between those two locations considering the waypoint(s) (optional field). The tool generates the results list with the objects that are both fully and partially positioned on the route. As soon as there is one common location between an object and the route, the object is listed.
6.1.1.2 General guidelines
Above the full list of the specified type of object are the options to import and object (+ Import) and create a new object (+ Add new ...) through the graphical user interface. In order to create an object, the user should click on the add new object button (“+ add new path” in the above example) and a new page opens.
General guidelines when creating and editing objects:
- Mandatory fields are marked with an asterisk (*)
- Circulation days and calendar: selection of the applicable weekday(s) and/or selection of the exact dates in the calendar. Note that if weekday(s) are selected, the calendar remains editable if specific dates need to be added/removed to/from the selection.
- Timetable period: timetable period, to which the object will belong when published
Line or route selection:
- The order in which locatons are added to the route is important as it indicates the running sequence of the object (start location on top). The order can be reversed with the reverse order feature (double arrows with opposite directions).
- The “From location” and “To location” shall be inserted by the user and the tool calculates the shortest route between these two locations considering the waypoint(s) (optional) field) and generates the timetable accordingly. As soon as there is one common location between two lines, the tool assumes the transfer of the train from one to another is possible.
- Timetable:
- Timetable refresh: when an object needs to be created on a shortened line, the timetable needs to be generated after entering the customised locations by clicking on the button "Generate Route"
- Times are mandatory: at the first and the last location (except for CNAs)
- Offset: automatically set if the tool detects a midnight crossing, but the user can also apply manual offsets, in case of a long dwell time at a station.
Relevant object-specific additional information is listed below.
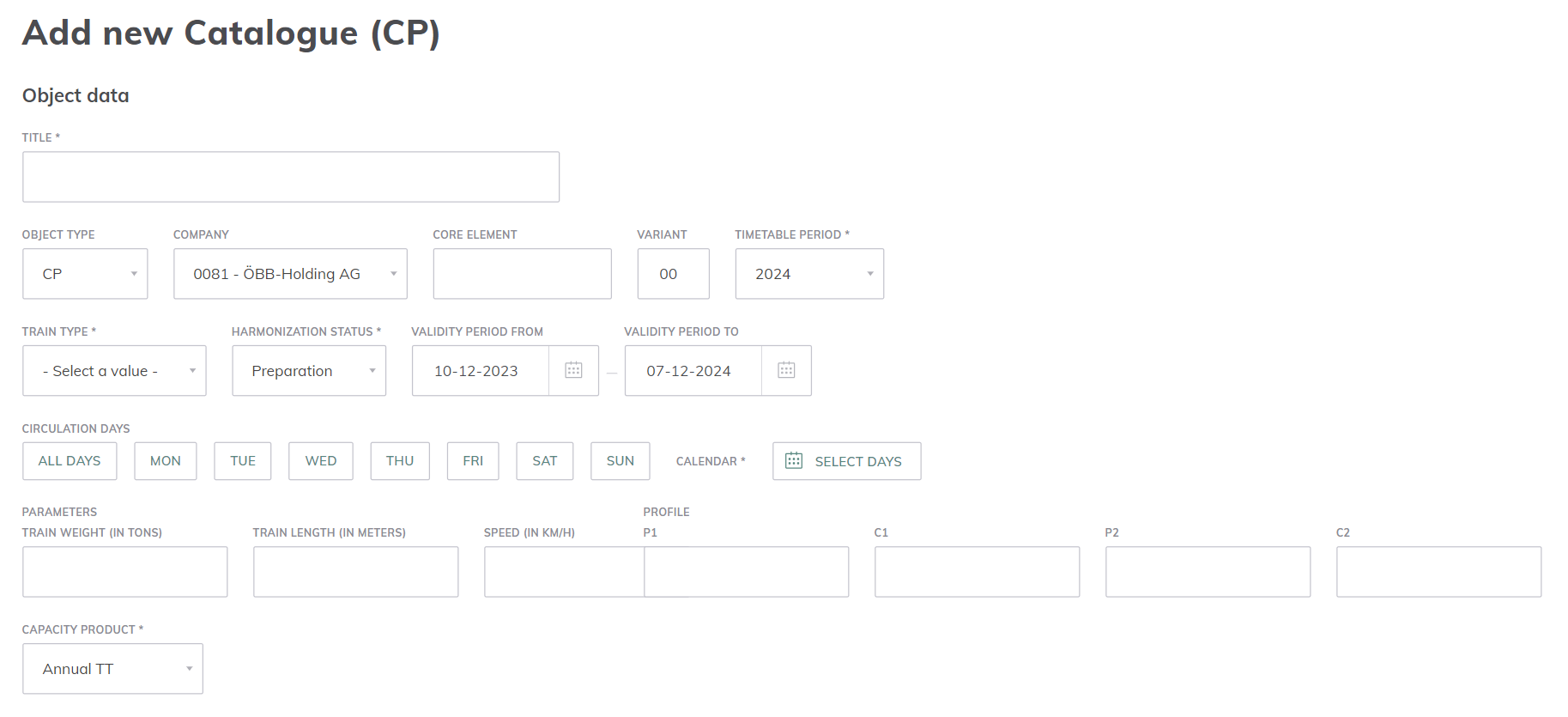
6.1.2. Add/edit Paths and Catalogue Paths
Paths and Catalogues Paths are two distinct objects in ECMT. However, the creation and editing of these objects is identical.
Train parameters are applied to the entire line if they are included in the object creation.
6.1.3. Add/edit Temporary Capacity Restrictions (TCRs)
- Validity period: TCR dates need to be defined within the validity period of a specific timetable period.
- Route:
- The route between two PLCs where the TCR takes place.
- Station closure: If the user wants to create TCR for only one station. "From location" and "To location" must be the same (positioning in yellow in the chart below for station B closure). Please note that the origin and destination station of a TCR are not considered as station closures.
- Temporal expansion:
- Continuous: the object will be shown from the first running “From time” until the last running day “To time”.
- Periodical: the object will be shown for all the selected running days with its “From”/”To” times
- Timetable:
- “From Time” and “To Time” refer to the timeframe within which the TCR takes place at the corresponding location. By default, “From time” and “To time” times are mandatory; if no exact timing is available when the object is created, 00:00 can be used.
- The start and end times of the TCR at the first and last locations can be different. Therefore, different TCR shapes are possible.
TCR characteristics can be defined with the following fields (click on the header of each characteristics section to open the additional values):
6.1.4. Add/edit Bandwidths
Bandwidths are spaces of time on a given route which are reserved for a certian number of slots. Bandwidths are visualised on the Capacity Supply alongside other Capacity Supply objects.
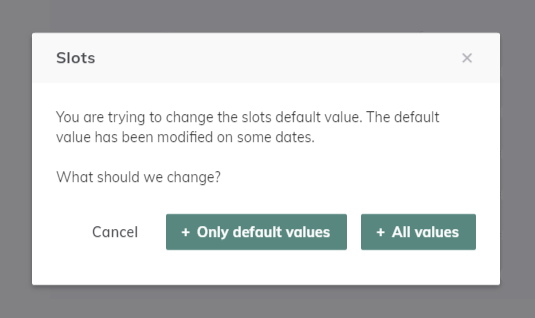
Slots refers to the number of capacities available within the bandwidth (the number of potential paths which will be included in the band).
If required, a different number of slots can be provided depending on the calendar. When editing the object after its creation, if the slot default number is updated, the tool will request confirmation on whether all dates need to be updated with the new default slot value or only those who were using the previous default value.
6.1.5. Object bulk operation
The bulk operation function is available when at least one object from the search results is selected.
After the objects are selected, button "Bulk operations" is enabled and clicking on it opens a new page.
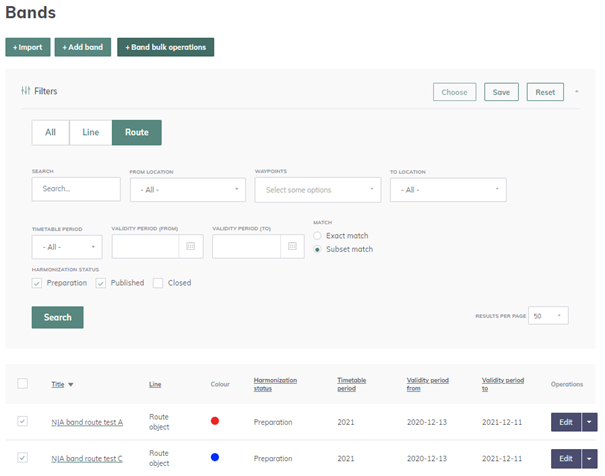
The operation needs to be selected by the user. Depending on the operation, input fields will change to enable the action.
All selected objects can be deleted in bulk by clicking on the "Delete" button.
6.2. Object import function
The import function is accessible when selecting any type of object in the 'Data' menu.
6.2.1. General guidelines
- Supported format: xlsx
- Each object type must be imported in a separated file.
- Export file and import file have the same structure. Exporting an object list containing at least one object per object type provides the required structure for the import file.
- The order of columns in the import file is irrelevant. Missing columns will trigger a warning and additional columns are ignored.
- Columns in the import file must have the same name as in the tool.
- The import file is not case sensitive.
- Time format: hh:mm
- Date format: dd.mm.yyy
- If applicable, an error message with the list errors will appear after the initial import of the file.
6.2.2. CataloguesPaths and Paths
Paths and catalogues paths have following import constraints:
- ID (mandatory): numbering common to rows belonging to the same object (minimun two locations, so two rows, shall belong to an object) and that do not yet exist in the tool for any object type. To identify the last already used object ID, the user should sorts the object IDs smallest to largest in the search function, finds the last number already used and uses the next ones as ID in the import sheet”.
- Title (mandatory): object title
- Colour (mandatory): 1 = red, 2 = green, 3 = black, 4 = blue, 5 = yellow, 6 = purple, 7 = brown
- Harmonization status (mandatory): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Traffic type (mandatory): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Line type: rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- TTP: number format, e.g. 2022. rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Valid from (mandatory with “Valid to” if no input in “Calendar”): to be in line with the TTP, if given. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Valid to (mandatory with “Valid from” if no input in “Calendar”): to be in line with the TTP, if given. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Line (mandatory if line-based object): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- OP (mandatory): location for the corresponding timetable shall in ECMT belong to the selected line.
- Arr: arrival time
- Arr offset: if applicable.
- Dep: departure time
- Dep offset: if applicable.
- For the following columns, number format and rows belonging to the same object must have the same input: Weight, Length, Speed, P1, P2, C1, C2
- For the following columns, 1 = the object circulates on that day; 0 = the object does not circulate: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday.
- Calendar (mandatory if no input in “Valid from” and “Valid to”)
- Object type: not mandatory and can remain empty or the correct abbreviation needs to be used: "PA" for the path, for catalogues "CP" = Catalogue path or "PP" = pre-arranged path
- Company
- Core element
- Variant
6.2.3. TCRs
- ID (mandatory): numbering common to rows belonging to the same object (minimun two locations, so two rows, shall belong to an object) and that do not yet exist in the tool for any object type. To identify the last already used object ID, the user should sorts the object IDs smallest to largest in the search function, finds the last number already used and uses the next ones as ID in the import sheet”.
- Title (mandatory): object title
- Colour (mandatory): 1 = red, 2 = green, 3 = black, 4 = blue, 5 = yellow, 6 = purple, 7 = brown
- Harmonization status (mandatory): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Line (mandatory if line-based object): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- From OP (mandatory): departure location. It shall exist in the system and belong to the selected line / route.
- From OP from time: arrival time at departure location.
- From OP to time: departure time at departure location.
- To OP (mandatory): arrival location. It shall exist in the system and belong to the selected line / route.
- To OP from time: arrival time at the destination location.
- To OP to time: departure time at the destination location.
- Bidirectional: 1 = yes, 0 = no
- Temporal Expansion (mandatory)
- TTP: number format, e.g. 2022. rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Valid from (mandatory with “Valid to” if no input in “Calendar”): to be in line with the TTP, if given. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Valid to (mandatory with “Valid from” if no input in “Calendar”): to be in line with the TTP, if given. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Classification
- For the following columns, 1 = the object circulates on that; 0 = the object does not circulate: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday.
- Affected estimated travel volume: percentage format without % symbol
- For the following columns, 1 = yes, 0 = no:
- Reduced Track Availability (LT)
- Reduced Track Availability (ST)
- Weight (W)
- Length (L)
- Profile (P)
- Total closure
- Speed restrictions
- No catenary
- Cancellation (freight trains)
- Cancellation (long distance trains)
- Cancellation (short distance trains)
- Cancellation (commuter trains)
- Rerouting (freight trains)
- Rerouting (long distance trains)
- Rerouting (short distance trains)
- Rerouting (commuter trains)
- Train/Bus Replacement (freight trains)
- Train/Bus Replacement (long distance trains)
- Train/Bus Replacement (short distance trains)
- Train/Bus Replacement (commuter trains)
- Estimated Delays (freight trains)
- Estimated Delays (long distance trains)
- Estimated Delays (short distance trains)
- Estimated Delays (commuter trains)
- Delay minutes (freight trains): number between 0 and 100 format
- Delay minutes (long distance trains): number between 0 and 100 format
- Delay minutes (short distance trains): number between 0 and 100 format
- Delay minutes (commuter trains): number between 0 and 100 format
- Object type: not mandatory and can remain empty or the correct abbreviation needs to be used: "TC" for the TCR
6.2.4. Capacity bands
- ID (mandatory): numbering common to rows belonging to the same object (minimun two locations, so two rows, shall belong to an object) and that do not yet exist in the tool for any object type. To identify the last already used object ID, the user should sorts the object IDs smallest to largest in the search function, finds the last number already used and uses the next ones as ID in the import sheet”.
- Title (mandatory): object title
- Colour (mandatory): 1 = red, 2 = green, 3 = black, 4 = blue, 5 = yellow, 6 = purple, 7 = brown
- Slots (mandatory): number format. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Harmonization status (mandatory): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- TTP: number format, e.g. 2022. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Valid from (mandatory with “Valid to” if no input in “Calendar”): to be in line with the TTP, if given. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Valid to (mandatory with “Valid from” if no input in “Calendar”): to be in line with the TTP, if given. Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- Line (mandatory if line-based object): rows belonging to the same object must have the same input.
- OP (mandatory): location for the corresponding timetable shall in ECMT belong to the selected line.
- From time (mandatory at origin and destination)
- From time offset
- To time (mandatory at origin and destination)
- To time offset
- For the following columns, number format and rows belonging to the same object must have the same input: Weight, Length, Speed, P1, P2, C1, C2
- For the following columns, 1 = the object circulates on that; 0 = the object does not circulate, Rows belonging to the same object must have the same input: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday.
- Object type: not mandatory and can remain empty or the correct abbreviation needs to be used: "BA" for the band
- Company: company creating the object
- Core element
- Variant